Building Gauge Charts in Power BI
Nov 23, 2020 • 6 Minute Read
Introduction
Gauge charts are used to show progress towards a particular goal. It helps understand to what extent a goal has been completed. Gauge charts are often used to represent key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales, revenue, manpower productivity, or profits. This guide will demonstrate how to build gauge charts in Power BI Desktop.
Data
In this guide, you will work with a fictitious data set of bank loan disbursal across years. The data contains 3,000 observations and 17 variables. You can download the dataset here. The variable used in this guide is the Loan_disbursed variable, which indicates the loan amount (in US dollars) disbursed by the bank.
Start by loading the data.
Loading Data
Once you open the Power BI Desktop, the following output is displayed.
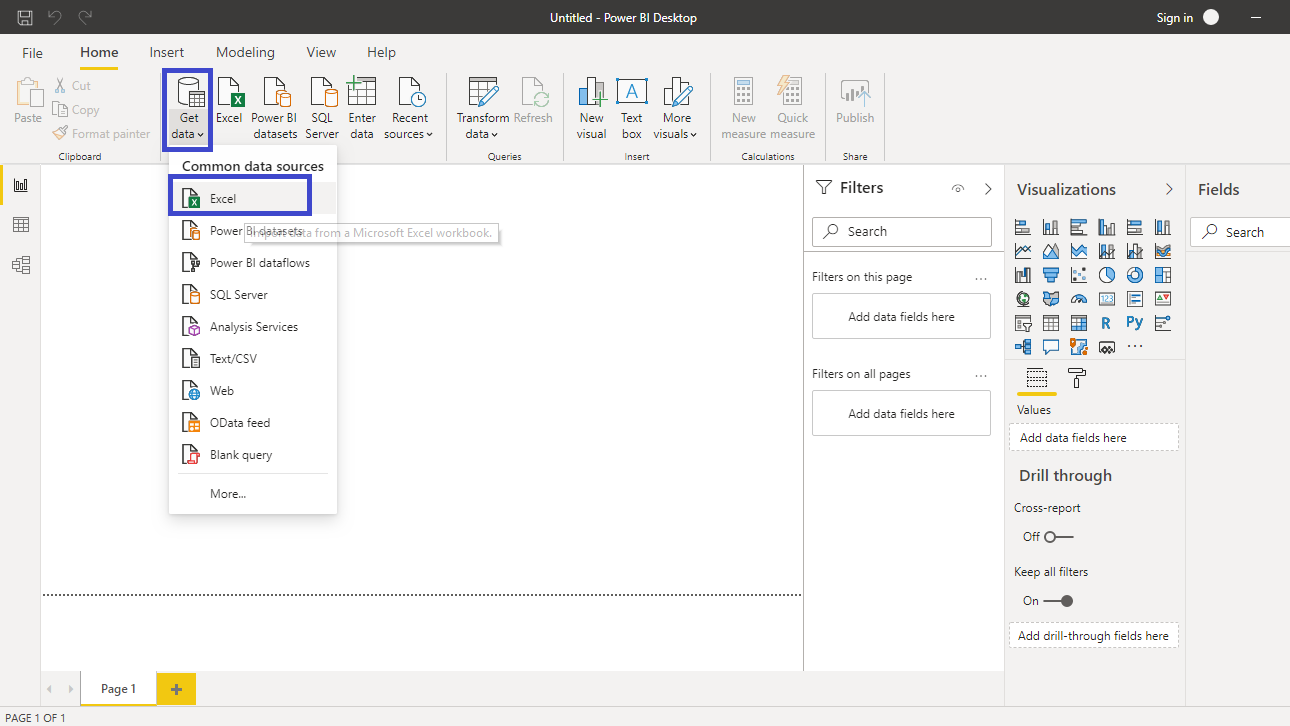
Click on Get data option and select Excel from the options.
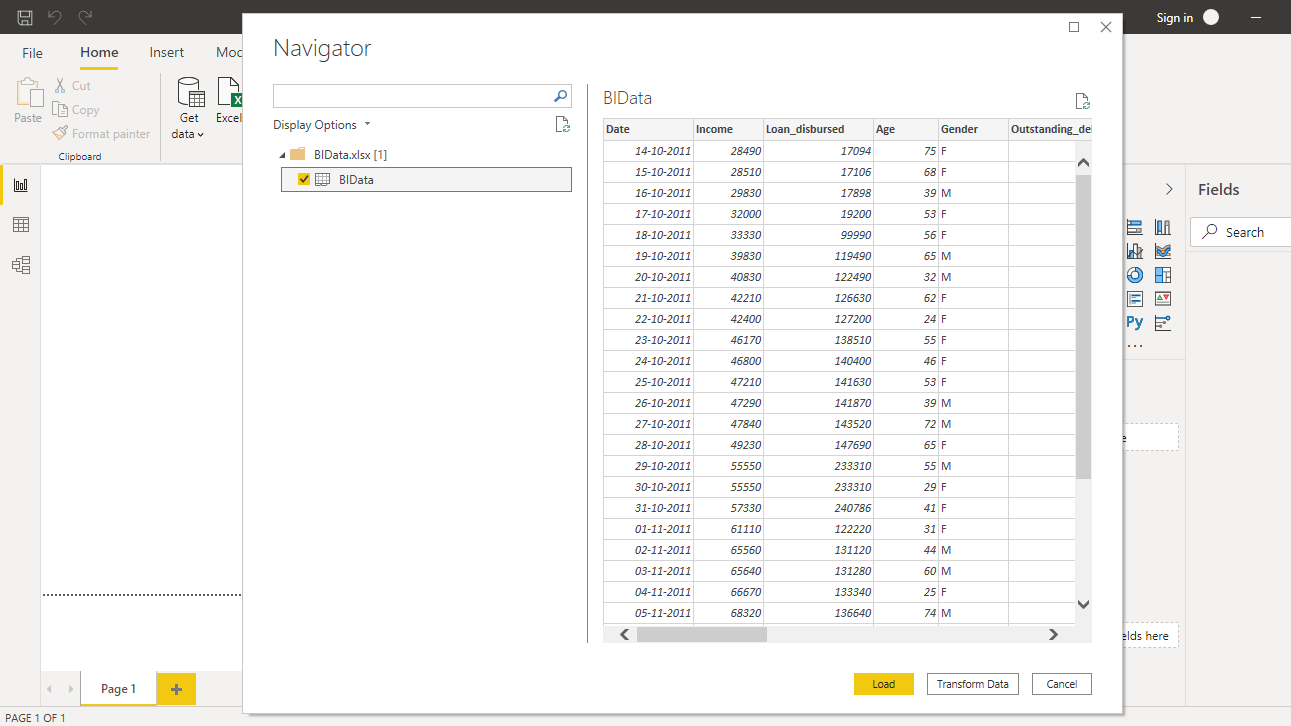
Browse to the location of the file and select it. The name of the file is BIdata.xlsx, and the sheet you will load is the BIData sheet. The preview of the data is shown, and once you are satisfied that you are loading the right file, click Load.
You have loaded the file, and you can save the dashboard. It is named PowerBI Visualization. The Fields pane contains the variables of the data.
Adding Visualization
To begin, you will need a chart, table, or matrix. You will create a Gauge chart in this guide. You can locate it in the Visualizations pane. Click on the chart and it will create a chart box in the canvas. Nothing is displayed because you haven't yet added the required visualization arguments.
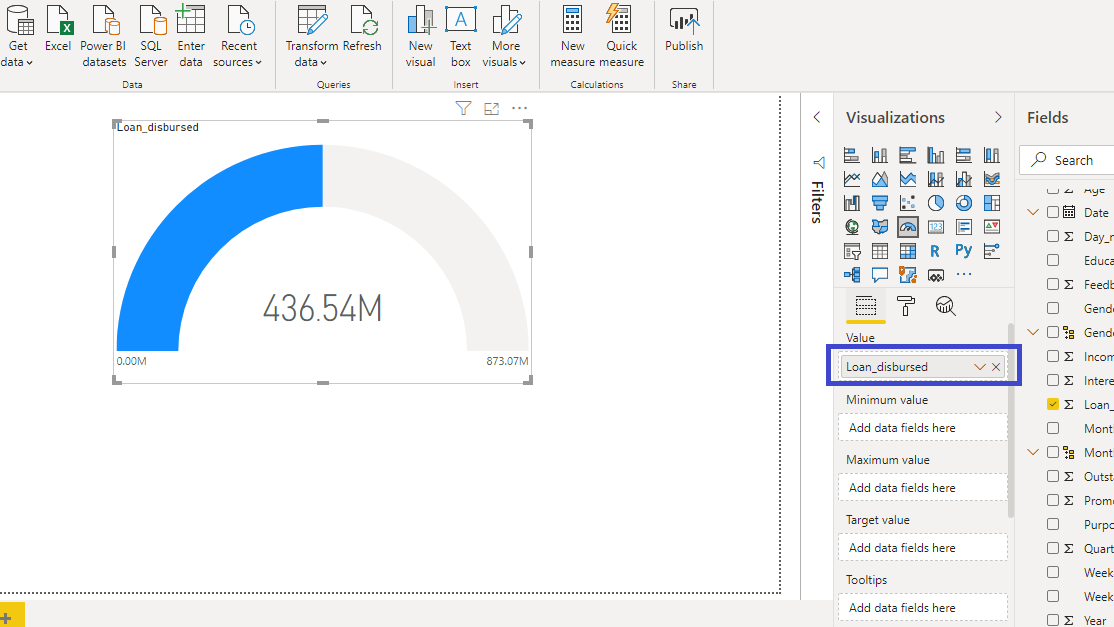
You can resize the chart on the canvas, and the next step is to fill the visualization arguments. Drag the Loan_disbursed variable into the Value field, which will create the following chart.
The output above shows that Power BI gauge chart automatically creates a target value. The default value is twice the total value of the measure, which is Loan_disbursed in this case.
Formatting the Chart
Under the Format pane, you will see various options of formatting the chart.
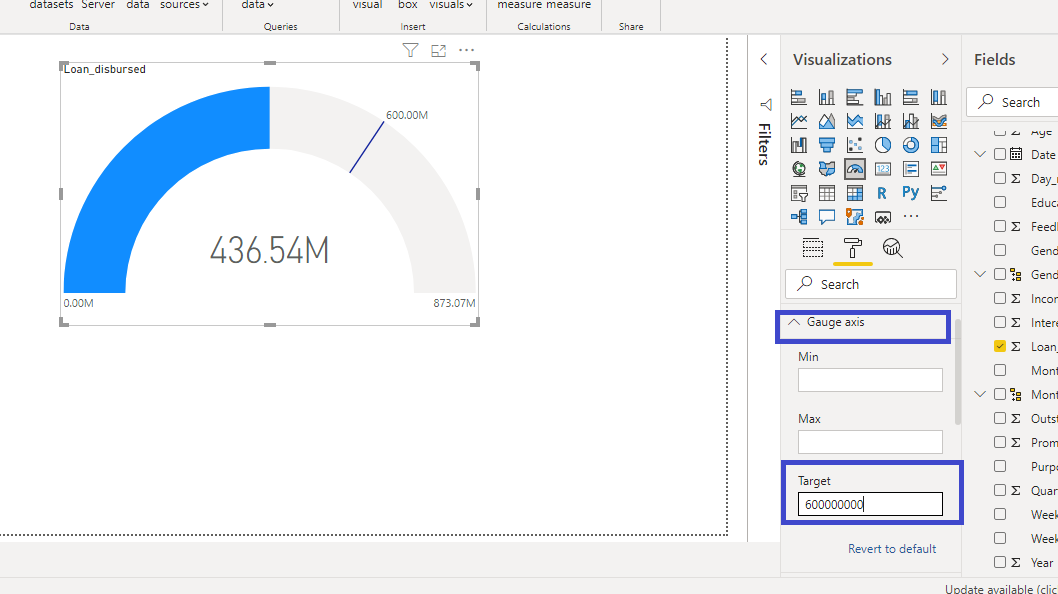
The first thing you can do is to set the target value in the gauge chart. Go to Gauge axis under Format, and set the Target value to $600 million.
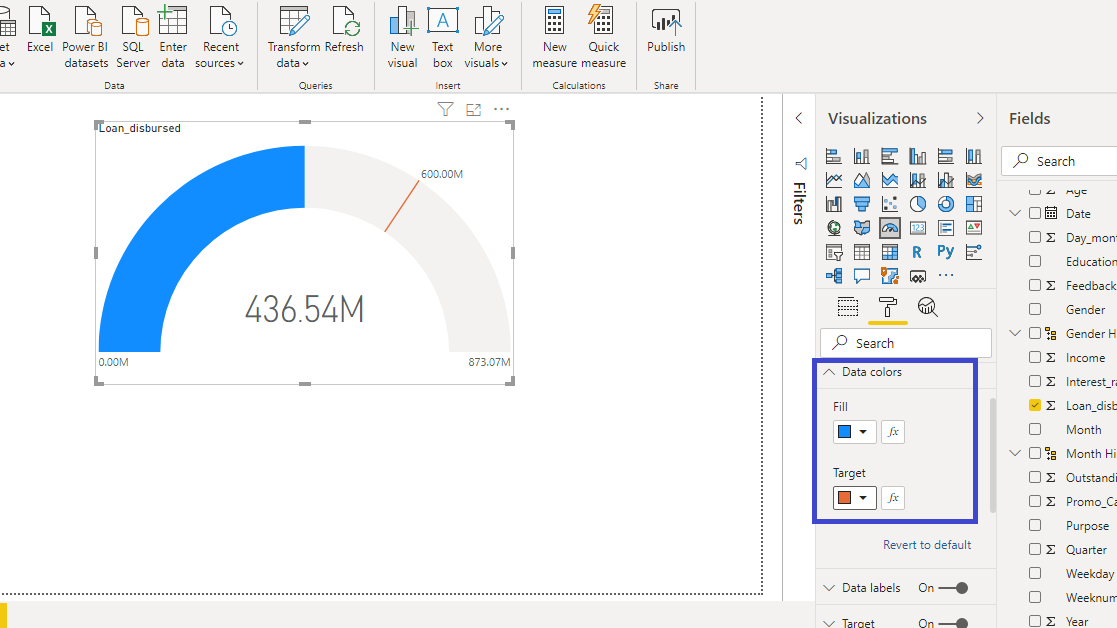
You can also change the Data colors to add contrasting color to the target value.
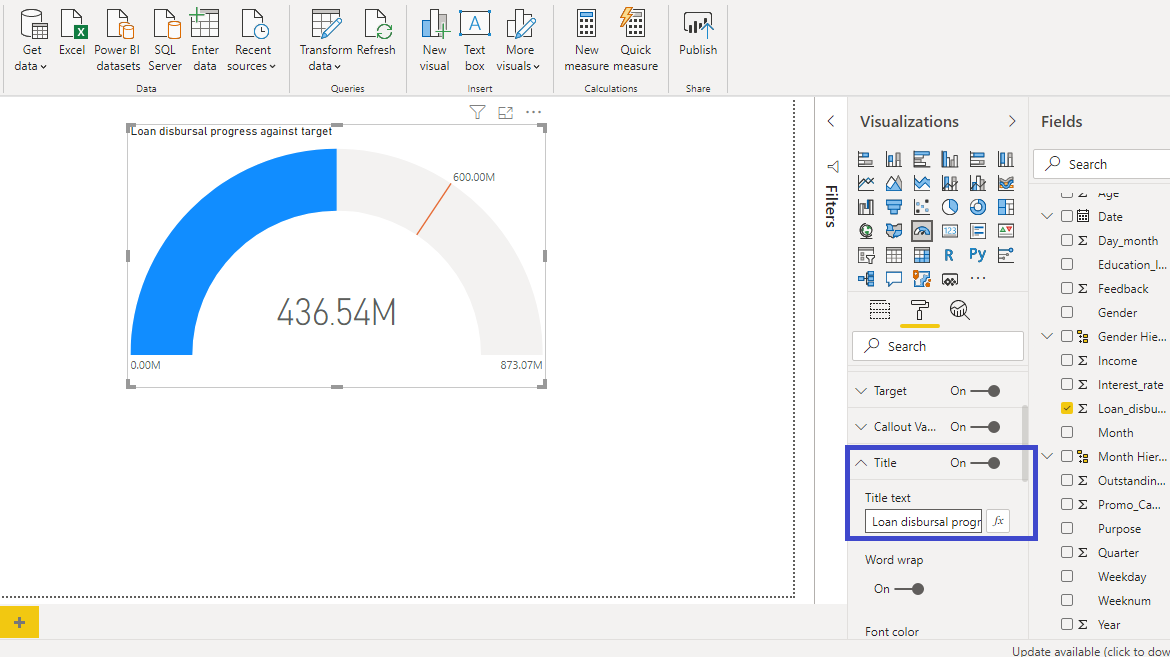
You might want to change the title of the chart. This can be done with the Title option.
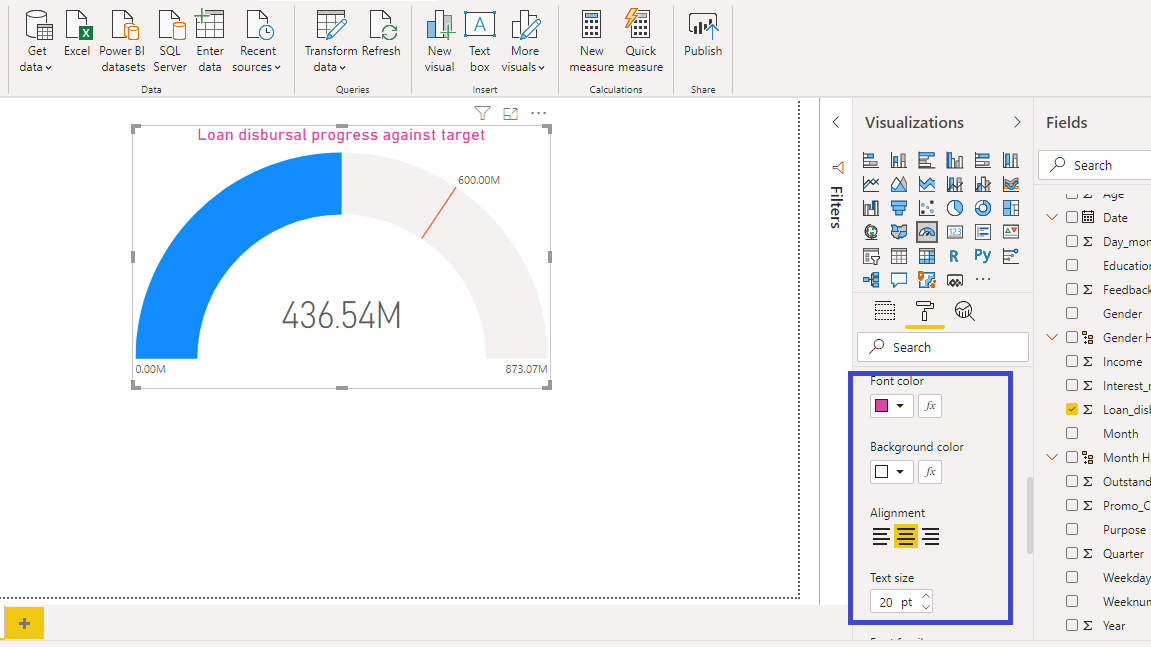
Finally, you can change the Font color, Alignment, and Text size of the chart.
The above output represents the resulting gauge chart, in which the loan disbursed by the bank is tracked against the target value.
Conclusion
A gauge chart is an important visualization chart in business intelligence and performance management. The gauge chart shows the minimum, maximum, and current value against the target value. This allows business leaders and managers understand the gap between the current and the target state, which allows them to do course correction, if required. This is an important chart type and the knowledge of building this chart in Power BI Desktop will improve your analytics and business intelligence capabilities.
To learn more about building powerful visualizations in Power BI desktop, please refer to the following guides:
Advance your tech skills today
Access courses on AI, cloud, data, security, and more—all led by industry experts.