- Lab
- Cloud
- Data
Import JSON into Cosmos DB
Azure Cosmos DB is Microsoft's globally distributed, multi-model database service. With a click of a button, Cosmos DB enables you to elastically and independently scale throughput and storage across any number of Azure regions worldwide. In this hands-on lab, we will export a table from our sample Azure SQL database to a JSON-formatted file. We will then use MongoImport to import this data into our Cosmos DB account as a new collection using PowerShell.
Path Info
Table of Contents
-
Challenge
Log into the Azure Portal and Prepare Azure Resources
-
Log in to the Azure Portal with the credentials provided.
-
Click on All Resources in the navigation hub menu and familiarize yourself with the Azure resources that have been provisioned, including:
- An Azure virtual network and network security group allowing SSH access to virtual machines
- One CentOS 7.5 virtual machine, along with supporting components (NIC, public IP, disk, etc.)
- One Azure SQL database and Azure SQL server
- One CosmosDB account
Obtain Public IP Address for VM Access
- Click on the virtual machine named lab-VM
- Inside the virtual machine blade, note the public IP address for this virtual machine.
Enable SQL Firewall Access to the Virtual Network
- Click on the SQL server named sqls-XXXXX, where XXXXX is a five-character unique lab ID for this lab.
- Inside the SQL server blade, click on Firewall and virtual networks.
- Click the + Add client IP button to add the IP of your local workstation to the SQL server firewall.
- Click Save to save the changes.
Log On to the Virtual Machine
-
Open up a terminal window on your local machine.
- For MacOS and Linux workstations, you can use the Terminal application.
- For Windows virtual machines, you may have to install an SSH client such as PuTTY.
-
In the terminal, connect to lab-VM by typing in the following (replacing
ip.address.of.vmwith the IP you noted earlier):ssh cloud_user@ip.address.of.vm -
Type yes to confirm connection, and enter the password for the virtual machine. The password can be located in the credentials section of the lab window.
-
-
Challenge
Install Database Tools on the Virtual Machine
Reference MongoDB repository
The
mongodb-orgpackage does not exist within the default repositories for CentOS. However, MongoDB maintains a dedicated repository. Let’s add it to our server.sudo suEnter the password for the virtual machine if prompted. The password can be located in the credentials section of the lab window.
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/linuxacademy/content-azure-az301-labs/master/mongodb-org.repo > /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org.repo exitInstall MongoDB Tools
Install the
mongodb-orgpackage from the third-party repository using the yum utility:sudo yum install mongodb-org-toolsEnter the password for the virtual machine if prompted. The password can be located in the credentials section of the lab window.
Enter y twice when prompted to confirm the installation and import the GPG key.
-
Challenge
Export the Customers Table from the SQL Database
- Back in the Azure Portal, click on All Resources, then on the SQL database named sqldb-XXXXX, where XXXXX is a five-character unique lab ID for this lab.
- Click on Query editor (preview) in the blade navigation menu.
- Sign in to the Azure database using the following credentials:
Username: acgadmin Password: S5w3R9Lbu*GvgfB5WWHg-
Enter the following T-SQL query into the window:
SELECT TOP (10) * FROM [SalesLT].[Customer] -
Click Run to execute the query.
-
Click the Export data as .json button to download a JSON file to your local workstation.
-
Open this file, named Query1.json, in a text editor on your local workstation.
-
Press Control+A on your keyboard (Command+A on MacOS) and then press Control+C (Command+C on MacOS) to copy the contents of the file to the clipboard.
-
Return to the virtual machine, and use the vi editor to create a new file:
vi customer.json -
In the vi editor, press i to insert new text into the file, and then press Control+V (Command+V on MacOS) to paste the text into the file.
-
Save the file by pressing Escape, then :wq, and then Enter. You will be returned to the shell.
-
Challenge
Import the JSON File into the CosmosDB Database as a New Collection
-
In the Azure Portal, click on All Resources, then on the Cosmos DB account named cosmos-XXXXX, where XXXXX is a five-character unique lab ID for this lab.
-
In the cosmos-XXXXX blade, click on Connection String. You will need information on this pane to complete this objective.
-
Return to the virtual machine, and run the following command to import the JSON file into the Cosmos DB account using
mongoimport:mongoimport -h exampledevto.documents.azure.com:10255 -d ImportedSQL -c Customer -u exampledevto -p YOURPASSWORDHERE --ssl --jsonArray --file customer.json- Replace
exampledevto.documents.azure.comwith the HOST value under Connection String in the Azure Portal. - Replace
exampledevtowith the USERNAME value under Connection String in the Azure Portal. - Replace
YOURPASSWORDHEREwith the PRIMARY PASSWORD value under Connection String in the Azure Portal.
- Replace
-
Your command should resemble the following:
mongoimport -h cosmos-dcru5.documents.azure.com:10255 -d Customer -c example -u cosmos-dcru5 -p 2vlxaaoaWcgKhGE1XAaNA1nBrvOnJzA299PyqyZDJxlo2PJFX9JNojxZZ5givkDUOsgR0KKwUvcjh16rmU9T5g== --ssl --jsonArray --file customer.json
-
-
Challenge
View Your Imported Data in the Azure Portal
Enable Cosmos Firewall Access to Your IP Address
- Click on the Cosmos DB account named cosmos-XXXXX, where XXXXX is a five-character unique lab ID for this lab.
- Inside the Cosmos DB blade, click on Firewall and virtual networks.
- Under the Firewall section of the pane, click the + Add my current IP button to add the IP of your local workstation to the Cosmos DB firewall.
- Click Save to save the changes.
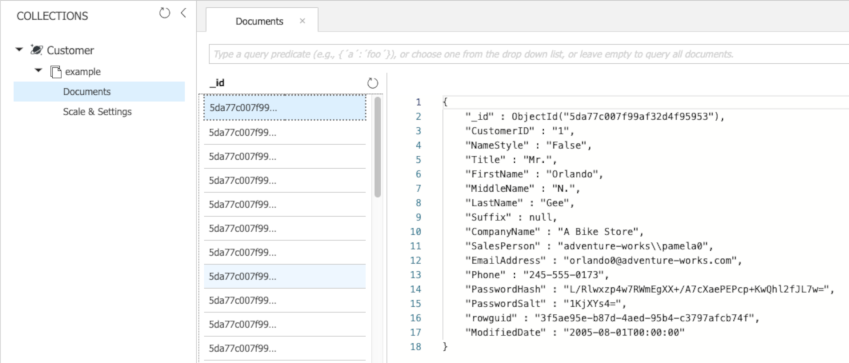
- While remaining in the Cosmos DB blade, click on Data Explorer. Note the new collection named Customer (you may need to refresh the collections).
- Expand Customer, and then click on Documents.
- Click on several of the documents that appear in the list and verify that they contain customer data.
What's a lab?
Hands-on Labs are real environments created by industry experts to help you learn. These environments help you gain knowledge and experience, practice without compromising your system, test without risk, destroy without fear, and let you learn from your mistakes. Hands-on Labs: practice your skills before delivering in the real world.
Provided environment for hands-on practice
We will provide the credentials and environment necessary for you to practice right within your browser.
Guided walkthrough
Follow along with the author’s guided walkthrough and build something new in your provided environment!
Did you know?
On average, you retain 75% more of your learning if you get time for practice.



